
The spine is made up of joints and vertebrae. Depreciation, mobility, nutrition are provided by the intervertebral disc and the joint capsule - a cartilage structure with fluid inside. The ligaments hold the complex structure of bone and cartilage tissue, limit hypermobility, and reduce the risk of dislocation. Muscle tissue protects against damage and delivers nutrients. For several reasons (age, injury, fatigue, changes in metabolism), the cartilage structure is erased and thinned. The joints are held together, the pressure in the spinal space changes.
The intervertebral disc is a dense, durable formation that is damaged as a result of incorrect joint positioning. When damaged, they leave their normal position, protrusion, hernias appear, which put pressure on the nerve endings. The process of autoimmune response begins - the body treats the hernia as a foreign formation that needs to be fought. Muscle cramps, impaired blood circulation, the person is in pain. Often the pain radiates to internal organs. Against the background of neuralgia, tachycardia, heart disease, lung, and unpleasant sensations in the abdomen appear. In women, there is difficulty in lifting the arms, tilting the head.

Osteochondrosis of the thoracic and cervicothoracic regions develops invisibly. Often, patients find out about the presence of problems during examinations when dealing with complaints about cardiac work. After examination, the neurologist makes a diagnosis of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis.
Osteochondrosis of the cervix-thorax
The first symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis can be detected independently at home. Changes in posture are the difficulty of keeping your back straight for a long time, discomfort in the shoulder blades, increased kyphosis - spinal deflection. There are 2 tests to detect problems in you.
How to detect the signs of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis:
Press your back against the wall as tightly as possible. Note the distance between the lower back and the wall. Usually, the back should be pressed completely to the wall. Large distances indicate the development of compensatory deflection - lordosis and kyphosis. Vertebrae and joints are mobile structures. Changes in one segment are compensated by leveling or deflection of another segment. Changes in women occur during pregnancy, when the spine adapts to the load while carrying a child. In women after 40 years, flattening the lumbar region, developing kyphosis in the chest is often noticeable.
Stand up straight. As you inhale, stretch the top of your head and hands up, as you exhale, bend over, reach the floor with your hands. Usually, hands should be free to touch the floor. If you do the exercise in front of a mirror, see how straight your back is when tilted.
Scoliosis, the problem of overweight, frequent colds aggravate the condition, giving rise to new severity. Degenerative-dystrophic processes occur more rapidly in weak areas. Over time, the symptoms of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis become more pronounced:
- stooped, inability to control proper posture;
- the appearance of a widow's hump at the level of the 7th cervical vertebra;
- discomfort under the shoulder blades (usually correct);
- chest pain when inhaling;
- difficulty in lifting arms, uniting shoulder blades;
- increased blood pressure, tachycardia.
Unfortunately, people do not always associate chest pain and symptoms of thoracic spine osteochondrosis. After reading the available recipes, self -treatment begins. Instead of massage and physical education, they take medication to reduce stress. Instead of chondroprotectors, mustard plasters are placed on the chest area.
Widow's hump
Widowed bumps, wrinkles, withering are the accumulation of fat in the cervicothoracic spine. Withering appears where the muscles are least developed. This is not just an aesthetic problem. Stagnation of the cervicothoracic region prevents free rotation of the head. In women with a widowed hump, the head is often sore, blood pressure changes, and there is a sensation of lumps in the throat. It is difficult to cut and separate the shoulder blades, the hands become numb, the eyes become dark, hearing is reduced, and when the head is turned, dryness is removed.
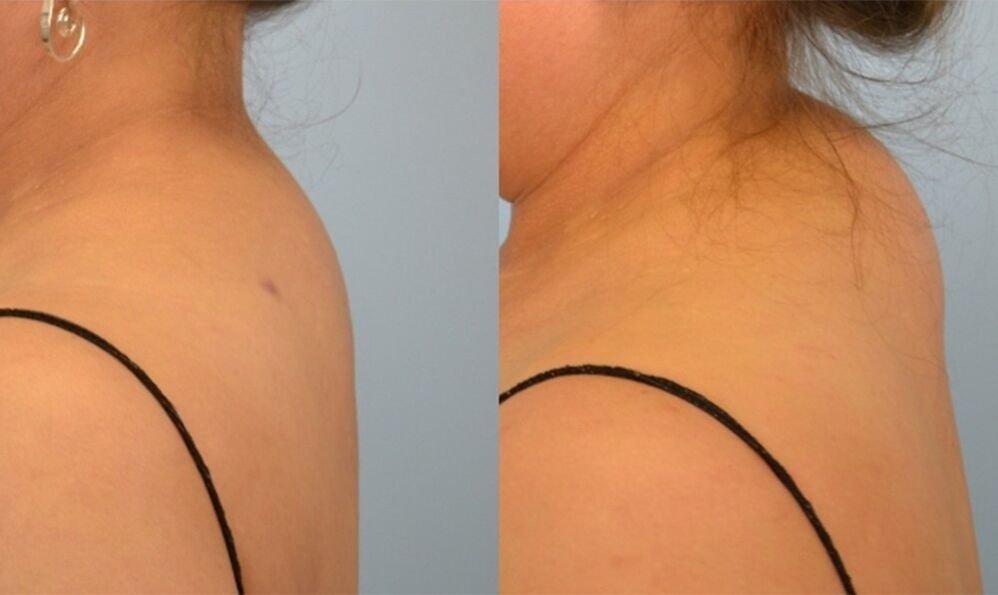
The disease gets its name because in women over the age of 45, doctors notice the formation of seals in the cervicothoracic area. Before this, at this age, women became widows. Today, signs of withering can be seen in overweight young women. In males, withering is not formed due to atomic features: developed trapezius, deltoid muscles and biceps.
Metabolic disorders, overweight, physical inactivity, weak muscles of the upper limbs form a wen. It is very difficult to get rid of the wilt that forms, need to do exercises, do massages, and follow a diet.
Bechterew's disease
A dangerous disease that occurs mainly in men, in which the muscles atrophy, the joints join. The biggest problem is that the disease is diagnosed at a late stage. It is very difficult to capture the moment of development, because patients come to medical institutions when the spine is already constrained.
Symptoms of pain first appear in the sacrum, and eventually to the neck. Deflection in the cervical-thoracic region increases, the body leans forward, acquiring the position of the applicant. Due to changes in chest position, it becomes difficult to breathe. Radiation of pain in the hands, increased blood pressure, muscle spasms torment the patient. Affected internal organs - heart, lungs, kidneys. Due to the wrong position, circulatory disorders hurt the eyes.
Timely diagnosis allows you to start treatment at an early stage. Taking medications (painkillers, muscle relaxants), exercise therapy, physiotherapy give good results. Patients need to put in a lot of effort to recover. In difficult situations, surgery is possible to remove the immobility.
Hearing loss
With cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, blood circulation in the brain is disrupted. Blood in the ducts stagnates, noise and ringing in the ears begins. There is an audio problem. The brain balances it by creating ghost sounds. Experiments conducted show that patients with circulatory disorders hear sounds, regardless of its presence. This is a protective system - if the ear is unable to capture some sound from the outside world, the brain creates this sound itself.
The severity of the disease is accompanied by congestion in the ears. In the presence of inflammatory processes - whistling, ringing, buzzing. In addition to hearing, vision deteriorates, memory is impaired.
Heart problem
During a spasm, the muscle compresses the vertebral arteries, which send blood to the brain. With a lack of nutrient fluids, the central nervous system gives a signal to increase the heart rate to increase stress. The heart beats faster, stronger, pressure increases, nutrition is restored.
Medication is taken to lower blood pressure - blood flow decreases, the heart starts beating faster again. Patients with osteochondrosis of the thoracic region rapidly develop cardiovascular disease. They may be bothered by discomfort in the chest area, which is exacerbated by moving the arms, taking deep breaths, twisting, tilting.

Dorsalgia - back pain, appearing due to pinching of nerve roots. Reflex muscle contraction exacerbates the condition - blood flow is disrupted, edema appears. It is important to provide yourself with timely medical treatment and consult a doctor for help with common pain.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
First aid for osteochondrosis is provided at home if you feel a sharp pain in your back, an unpleasant sensation in the chest area, it is difficult to lift your hands and move.
You need to take NSAIDs. Remember that with osteochondrosis, medications with anti-inflammatory effects help better. Analgesics are less effective, although they have few side effects. Rub NSAID ointment or chondoprotector ointment into the site of inflammation. Massage movements will spread the blood, relieve swelling, and medication will help you survive the worsening condition. You have to move through the pain - make circular movements with your hands, head, hips, bring your shoulder blades close. Stretch your back by leaning against a table or chair.

Warm compression is not recommended. After all, the blood will flow faster to the site of edema, it will not be able to pass through the ducts due to muscle spasms. As a result, the swelling will increase, the inflammation will spread. For pain in the thoracic area, stretch the spine on a horizontal bar, or with a Glisson loop. Correction with active traction is only used with well -developed muscles, and also there is no need to strive for a state of complete rest.
If the deterioration recurs within a month, it is better to see a doctor for examination, diagnosis and treatment. It is impossible to fully recover from osteochondrosis - there is no technique that allows you to turn back time and stop the degenerative process.
But there are techniques that will help to cope with pain and adapt to constant change. These are drug treatment, massage, physiotherapy, manual therapy, vertebrorevitology, acupuncture and kinesiology.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will choose a recovery option: prescribe the necessary medications that will help you survive the depression, recommend procedures and manipulations for recovery.


















