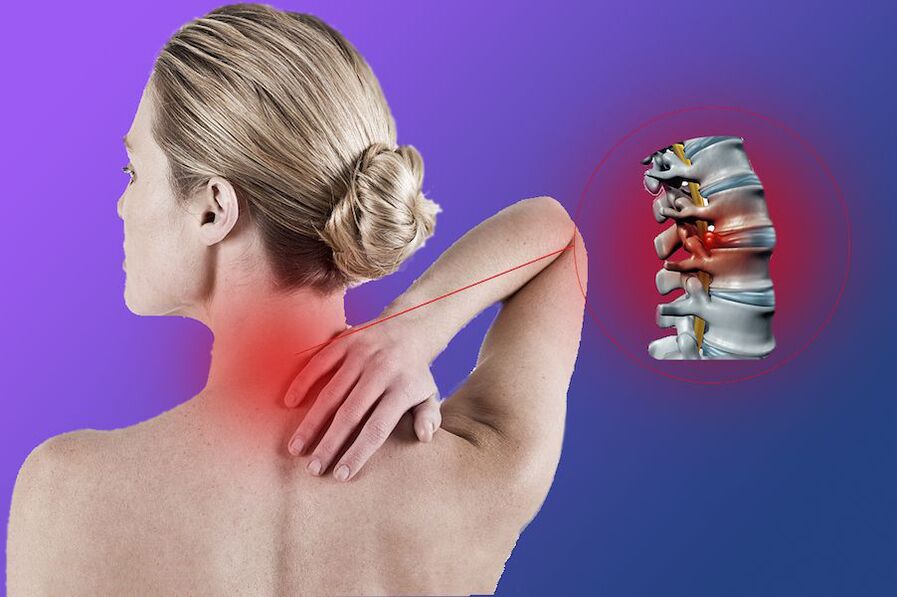
Cervical osteochondrosis is a complex of degenerative disorders in the upper part of the spine, causing damage to the intervertebral disc, changes in its texture and function. More often, the discs at the level of the fifth, sixth and seventh vertebrae undergo degenerative changes, because this area of the spine is more mobile, it is most involved in the movement of the head, which means it experiences a high load. As a result of this disease, there is a thinning of the intervertebral disc, violation of blood supply to the spinal space, pinching of nerve roots, which causes pain.
People of any age can develop osteochondrosis, but more often the disease occurs in 30-50 years. Before the onset of the first attack of pain, the effects of cervical osteochondrosis are almost insignificant - discomfort and some heaviness in the neck, dizziness, twinkling stars in front of the eyes. Often people do not know the true cause of the disease. But the sooner a diagnosis is made and efficient treatment initiated, the greater the chance of a full recovery. Timely treatment of neck osteochondrosis will help restore good health and provide health in the future.
Signs, symptoms and treatment of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis has its own characteristics due to the structure of the vertebrae and their size - they are much smaller than the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, and also less durable. Due to poor neck muscle development, the vertebrae experience increased stress and are more prone to injury.
Regardless of the stage of development of modern medicine, the pathogenesis of this disease is not fully understood. Changes in vertebral body structure and intervertebral discs are facilitated by metabolic disorders in the body, inactive lifestyle, poor posture and curvature of the spine, overweight, infectious diseases, hypothermia, stressful situations, improper exercise, and injuries.
Stages of disease development
- With first -degree cervical osteochondrosis, the pain is still insignificant. During this period, there is discomfort in the neck after prolonged exercise and tension in the muscular ligaments. All this can be corrected with the help of physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapeutic procedures, ointments and taking vitamin complexes.
- With second -degree osteochondrosis, when pinching of nerve endings and the appearance of disc protrusion are possible, the pain becomes severe, especially when a person is standing. Periodically dizziness and darkening of the eyes. In addition to physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory and painkillers become necessary.
- The third stage is characterized not by paroxysmal, but by persistent pain, spreading to the shoulder and upper limb areas. Due to the appearance of a hernia, numbness of the hand muscles and temporary loss of finger sensitivity are possible, joint mobility worsens. In some cases, during the third stage of the disease, surgical intervention is required.
- With fourth -degree cervical osteochondrosis, the pain subsides, but this is by no means the beginning of recovery. At this time, almost complete destruction of the intervertebral disc occurs, osteophytes grow at the junction of the vertebrae, which injure the vertebrae and nerve branches. Brain nutrition worsens, as a result dizziness appears, tinnitus occurs, vision decreases and movement coordination is impaired.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
The symptoms of osteochondrosis may vary depending on which segment of the spine is damaged and the degree of damage. Most people feel pain in the neck, above (to the chin) and, conversely, below - in the area of the shoulder girdle, arms, chest. May be numbness of the fingertips and tongue, general weakness, increased pressure, decreased visual and auditory acuity, throbbing when moving the neck.
With cervical osteochondrosis, the characteristic symptoms are:
- Root Syndrome. When the nerve is pinched, the resulting pain passes from the neck to the shoulders, spreading to the forearms, hands, fingers, and swelling appears. The firmness and elasticity of the skin deteriorates, due to poor blood supply, it becomes pale.
- Vertebral artery syndrome is indicated by throbbing pain in the back of the head, crown, affecting the temporal head lobes and the superciliary region. The pain can increase if the head is in an uncomfortable position for a long time, for example, on a truck driver who must constantly monitor the road while driving. Probably the appearance of nausea, dizziness, deterioration of vision and hearing, damage to the vestibular apparatus.
- Cervical migraine syndrome occurs when the branches of the sympathetic nodes are irritated. When exposed to nodes, there is a violation of the work of cerebral vessels, a deterioration in blood supply to tissues. Patients experience increased pressure, increased heart rate, noise in the head, congestion and ringing in the ears.
- Hypertensive syndrome is characterized by an increase in intracranial pressure. The patient feels a headache that breaks from the inside, nausea, vomiting may occur, body temperature rises, ESR increases.
Why is osteochondrosis dangerous?
The sooner treatment of neck osteochondrosis is started, the more likely it is to stop its progression and get rid of the disease. In further cases, when an irreversible process has occurred, treatment will only help relieve pain and inflammation. What is dangerous osteochondrosis and what disease development can be triggered:
- intervertebral protrusion and hernia;
- vertebrogenic cervicalgia (limited neck mobility);
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- migraines and severe headaches that do not go away even after taking modern painkillers;
- visual and hearing impairment;
- paresis;
- osteophyte formation;
- deterioration of blood supply to the brain and more.
Disease treatment
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can be effective only if it is comprehensive and includes:
- drug treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae, aimed at reducing pain and inflammation;
- physiotherapy procedures;
- medical gymnastics;
- manual therapy methods;
- in extreme cases, when conservative treatment does not help and the patient’s condition worsens, or if limb paralysis occurs, surgery is performed.
Identifying the cause of cervical osteochondrosis by specific symptoms and treatment is not a quick process. Depending on the patient's immunity, body condition and stage of the disease, a course of intensive therapy can last from 1 to 3 months, and then maintenance procedures are carried out for about a year.
Medical therapy
Drug treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine aims to:
- pain reduction;
- removal of inflammation;
- eliminate swelling;
- better metabolism;
- suspension of degenerative processes and tissue regeneration.
Currently, medications have not been developed that will address all tasks at once, so doctors may prescribe the intake of several medications at the same time.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are among the drugs aimed at relieving pain and inflammation in the treatment of cervical vertebral osteochondrosis. Antispasmodics help relieve cramps and reduce pain. Non -steroidal ointments and topical gels also help relieve pain. Diuretics are prescribed to reduce swelling.
During the treatment of cervical and brachial osteochondrosis, it is necessary to use drugs that improve the function of the musculoskeletal system, stimulate metabolism and tissue regeneration, drugs that prevent irreversible changes in the joints. These agents include chondroprotectors, vitamin C and vitamin B.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine
Physiotherapeutic procedures have a local effect on the damaged area, improve blood microcirculation, relieve swelling, inflammation, and relieve pain. Depending on the course of the disease, the doctor may prescribe:
- exposure to low frequency currents and electrophoresis;
- massage, including hydromassage (especially useful during the recovery period);
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound treatment,
- therapy with a "soft" laser beam.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is not used at all stages of osteochondrosis and is not for all patients, therefore, a qualified specialist should prescribe and carry out treatment. For example, its implementation is prohibited in the event of infectious diseases, benign and malignant tumors, blood diseases and intervertebral hernias. What are the positive effects of this method of therapy? After the required course of treatment, the signs and symptoms of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis such as pain, numbness of the hands, dizziness and tinnitus disappear. The manipulation performed relieves tension in the neck muscles, improves blood circulation and strengthens the immune system.
Treatment of diseases at home
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis at home is quite acceptable and can be no less effective than in a hospital, but a specialist should prescribe it and monitor the course.
In a relaxed home environment, it is easy to do a set of physical therapy exercises. Gymnastics will help strengthen the neck muscles, improve blood circulation, and in turn nourish the vertebrae, and reduce pain. The main thing in home treatment is a systematic procedure. All exercises should be performed smoothly, avoiding sudden movements, gradually increasing the load and intensity of training. If during gymnastics the condition worsens, the pain increases, it is necessary to reduce the rhythm of the lesson and range of motion.
Folk remedies for osteochondrosis
Traditional medicine also offers its solutions in the treatment of cervical and brachial osteochondrosis: the use of infusions and decoctions, therapeutic baths, rubbing in oil, homemade ointments and scrubs.
- To reduce pain and relieve inflammation in the evening, before bed, take a leaf of carrot, steam in boiling water for a few minutes, cool slightly, then attach it with the inside to the neck and wrap with a warm scarf. Leave overnight. Cabbage leaves are also suitable for therapeutic compresses, only they are not steamed before use, but lightly beaten with a kitchen hammer.
- To relieve unpleasant symptoms and treat osteochondrosis of the neck, make a honey-potato compress once a week. Grate 2 potatoes on a fine grater, add ½ tsp. Honey, mix well. Apply the resulting slurry to the affected area for one and a half to two hours, wrap your neck and try to lie down without moving. Then wash the porridge with warm water.
- Rub for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the neck and relieve symptoms: take ½ cup of elderberry and 2 cups of alcohol, leave for a week in a well -closed container in a dark place. Rub the resulting product into the cervical collar zone.
- Decoction of elecampane root is used to provide anti-inflammatory compresses. 2 tablespoons biennial elecampane pour 1 cup boiling water, simmer for 10 minutes, then cool and strain. Apply a compress of warm boiled water to the cervical collar area twice a day (morning and evening) and keep for about 20 minutes. It is also useful to bathe with a decoction of elecampane (for bathing, you need to prepare a decoction of 10 tablespoons of the plant).
- A no less effective way to reduce inflammation, eliminate the causes and symptoms in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is an ointment from hop cones. To prepare it, take 1 tbsp. ground hop cones, rub well with 1 tbsp. butter or lard. Lubricate the affected area with the resulting product, then cover with a napkin and wrap with a warm scarf. Daily use of the ointment will quickly bring the desired result.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis with laser devices
At home, you can not only take medications prescribed by a doctor and do a set of exercises, but also continue physiotherapy, for example, paraffin bandages or laser beam treatment. A unique portable laser device has been developed for the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Its action is effective in the acute period of the disease and in the remission stage. Treatment of osteochondrosis with a "soft" laser beam will quickly relieve neck pain, reduce inflammation, swelling and improve overall well -being. To achieve its effect, it is necessary to act on the line along the damaged vertebra 2-4 times a day for 18-24 minutes, and then in the direction from the vertebrae to the earlobe.


















