What is this disease with a complicated name - coksartrosis?.. This disease is a hip joint deformation arthrosis and is often called osteoarthrosis of the hip joint.Currently, coksartrosis is a leader in the disease of the musculoskeletal system, which is degenerative-dystrophic.There are many reasons for the occurrence of coxarthrosis and in this case, the disease has become extensive in all age groups.
Coksartrosis belongs to arthrosyses that have no inflammation, in the beginning there is a change in degenerative-dystrophic properties in the cartilage of the hip joint, which includes the articular bone surface, and at the later stage there is a direct bone change.In such a way, gradually developing coxarthrosis, there is a violation of normal functions naturally from the affected hip joint, which, in the end, leads to a violation of the functional musculoskeletal equipment of the sick, in general.
For the most part, hip joint arthrosis is experienced by people who are forty years old.Of course, coxarthrosis, like other diseases, may seem to be able to treat without surgical intervention, but only in the early stages.But in the future, it is not possible to do without surgery, and only one thing can help prevent defects - prosthetic coxarthrosis joints.Unfortunately, people who are sick, without attaching small pain in the hip joint in the early stages of the disease, avoid finding a doctor, and osteoarthritis hip joint, continuing to advance day by day, gradually turning into a more neglected form.
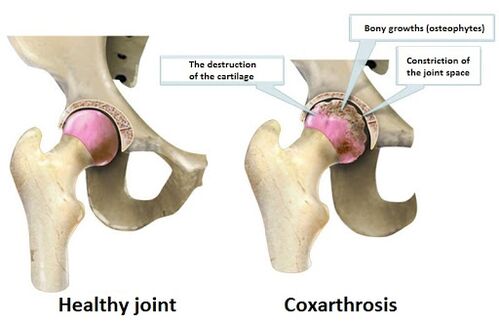
How Coksartrosis develops
Let's take a look at the mechanism of development of coxarthrosis disease.And we start with the fact that the hip joint is made up of two bones:
- the most female end, the same as the ball;
- Swivel, similar to a small biliary troupe located on the pelvic Iliac section;
- Special joint cartilage on the second surface -both bones, resembling materials such as sponge and necessary as a shock absorber, which is compressed during movement and straightening it;
- as well as the ligaments that form the hip joint cavity and thus form a joint capsule.
Surrounded by joints, in addition, there are muscle tissue, somehow femoral, gluteal and other muscles, where the function of the hip condition also depends.
During movement, when compressing the articular cartilage, certain fluids are "squeezed" into the joints, which is a type of lubricant for bones that are articulated in the joints.Also, the articular cartilage itself, in addition, performs the uniform distribution function of the load to the surface of the joint, becoming an excellent shock absorber during movement.
The occurrence of coxarthrosis, mainly due to the fact that the power of the cartilage of the hip joint is interrupted.The cartilage becomes thinner, and then disappears in place.If you do not take steps to stop this process, then in places where the cartilage described above occurs, the bone itself will grow directly, thus trying to "fill" the void of the joint cavity itself.As a result of such changes in bone, therefore, osteophytes began to appear, that is, "spikes" in the bone.These modifications, in turn, lead to infringement of bone congruen that are articulated in the hip joint and "abrasion" from the healthy parts of the articular cartilage.
Causes of arthrosis of the hip joint
The causes of coxarthrosis in which they arise can be divided into primers, which have unclear etiology, and secondary, as a result of other diseases, for example, such as:
- thigh dislocation, natural;
- femoral displacement;
- Femoral aseptic necrosis itself;
- Previously moved various injuries, such as the broken neck of the thigh;
- Middle disease;
- the process of inflammation in the hip joint;
Because coxarthrosis disease is found not only for one, but at the same time the two hip joints, it is very possible to say that bilateral coksartrosis is rare.Even with the main coxarthrosis, usually the knee or spinal joint is also affected.
Symptoms of coxarthrosis
The first symptom of coxarthrosis directly depends on the degree of damage to the hip joint, as well as at the developmental stage of the disease, and the main thing is:
- The pain shown during movement, in the hip joint, and disappears at rest;
- arise;
- stiffness that appears in the hip joint;
- Progress below the hip movement amplitude;
- Femoral muscle weakness and significant decrease in their numbers.
Separately, we consider the symptoms of coxarthrosis depending on the level of the disease with the disease:
- Symptoms of the first stage of coxarthrosis: in the hip joint there is a moderate pain, and only after the joint is subjected to an intensive load for a long time.After removing the load and rest, the syndrome is completely stopped.In the first stage, the symptoms of Gait Coksartrosis remain normal and the amount of joint movement has not changed.
- Symptoms of the 2nd level of coxarthrosis: pain in the hip joint is felt more intense than in the first stage, but in addition, they are projected into the inguinal region.Due to the developing muscle atrophy, the knees begin to ache and knees, and are quite frequent.Sometimes, with the symptoms of second -degree chocolate, pain begins to occur at rest, and after the load on the affected joints, a relatively long rest is required to stop it.The closing begins to appear while running or walking for a long time.At the same time, the strength of the hip muscles is reduced, and the amount of joint movement is also underestimated.
- Symptoms of the 3rd level of coxarthrosis: the pain syndrome that is constantly pronounced in the hip joint, does not pass even after a very long or regular rest at rest, even at night.The pain has been completely affected by the whole leg.Against the background of pain, the sick man suffers from insomnia and various sleep disorders.There is a strong atrophy of the thigh muscles, buttocks and lower legs, while the number of joint motors is almost minimal.When walking, the sick person to move had to use additional methods, such as sticks for example.
If the arthrosis of the hip joint only develops in the hip joint of one foot, then the weak femoral muscles give a boost to the development of the pelvic side displacement, which is the length of the foot with the joints affected by coxarthrosis.
Diagnosis of coksartrosis
When performing the diagnosis of coxarthrosis, the symptoms of coxarthrosis, described above, combined with the data obtained by the patient's X -ray examination, are taken into account.Such techniques provide the possibility of determining not only the level of coxarthrosis, but to identify the causes of the catalyst for the development of coxarthrosis.Radiography provides a good opportunity to determine specific changes causing injury to the hip joint area, which is directly related to the developmental mechanism of coxarthrosis.
In addition to the listed diagnosis methods, calculated tomographic methods and magnetoresonance imaging can also be used, providing a possible study of developing pathologies, such as, for example, bone tissue, deformation that is the satellite of the disease.For magnetic resonance imaging, this method still enables the assessment of pathological disorders in which the soft tissues around the joints affected by coxarthrosis have been subject to.

Treatment of hip joint arthrosis
The choice of treatment for coksartrosis directly depends on the symptoms of the disease and its stage.Usually, at the first and second levels of the hip joint, traditional-conservative drug therapy is performed, consisting of the intake of chondroprotectors, vasodilating drugs and, according to the guidance, also relaxed muscle.During the period when coxarthrosis is an anti -inflammatory drug, not -steroid is also used.Keep in mind that such treatments must be done by experts, as their own drugs, unlike traditional medicine, can have a very negative effect on the patient's internal organs and fully suppress the ability to restore hyaline cartilage.
Also, with hip joint arthrosis, various physiotherapy procedures and exercise therapy are prescribed.
Especially effective, combined with the treatment of traditional hip joint arthrosis, is the use of magnetotherapy methods.The early method of magnetotherapy is very effective - it prevents dystrophic changes and revives the disease.In later stages, this method improves performance and quality of life, reducing the risk of complications in the affected joints.
The effects of the patient's body with coxarshrosis do not have a direct therapeutic effect with the diet, but it is recommended for obese people to lose weight, as it allows to reduce the burden on the affected joints, thus facilitating acute symptoms of coxarthrosis.
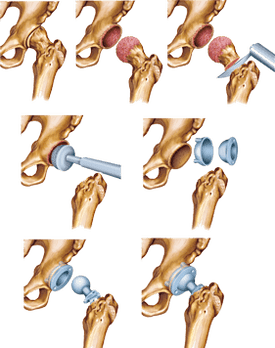
For the third stage of coxarthrosis, the most painful symptoms, treatment, therefore, is performed only through surgical intervention, for example, endoprosthetics hip joint is performed.
Endoprosthesis includes components that are functional analogs of the hip joint.This orthopedic product is installed within the limbs, which is determined by its name (Endo - from the "internal" of Greek).Artificial substitutes for hip joints perform musculoskeletal function, but unlike the natural joints in it, lubricant fluid does not occur.Yes, it is not necessary, as the prosthesis is made of materials that, without any lubrication, slide easily and do not destroy.
Statistical data shows that after surgery, the absolute recovery of the functioning of the limbs with the deformation of the hip joint arthrosis is achieved in 95% of cases, which allows to then bring a relatively active lifestyle.
The life of such prostheses is about 15 ... 20 years, but at the end of its service, the second operation is required to replace the use of endoprosthesis.
Please noteIt's important!Don't diagnose yourself!In the case of coxarthrosis symptoms, you should consult an orthopedic doctor, as only a qualified specialist can make the right diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment.
Prevention of coxarthrosis
Coxarthrosis disease can also be avoided if the prevention of coksartrosis is required:
- mandatory and timely treatment of inflammatory joint disease;
- Treatment of displacements together on time;
- Proper and reasonable physical activity, especially weight training that needs to be done correctly;
- Mandatory control of your weight, with its usual maintenance;
- Prevention of joint injury.


















